Successful ERP implementation requires a strategic approach that aligns with your business goals, ensuring minimal disruption and maximum efficiency. This guide breaks down the critical steps and best practices for navigating your 2024 ERP implementation, helping you avoid common pitfalls and achieve a seamless transition.
With a clear plan in place, your business can unlock the full potential of ERP to enhance productivity and drive growth.
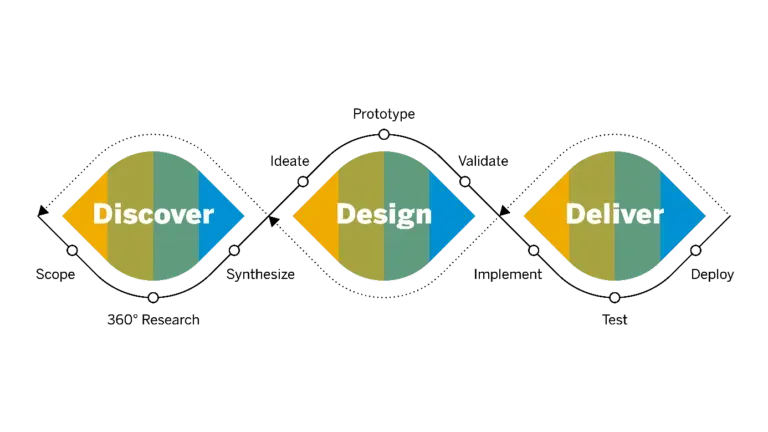
ERP Implementation Phases and How to Make it a Success
ERP implementation phases are very critical for the success of your ERP system. If you do not follow any of these phases in the manner prescribed below, your implementation process can turn out to be a disaster. Therefore, you should carefully follow each of the 10 ERP implementation phases listed below.
Phase 1. Initiation and Discovery
This step gives your process a strong foundation and so, you should carry it out well. It involves extensive research to collect information on the current systems and processes of your business.
This will help the software understand the basic problems that might occur. You can create a discovery team for this purpose. This team will comprise senior stakeholders, project managers, technical leads, external consultants, and representatives of departments.
Phase 2. Requirement Analysis
Once the discovery team has gathered all required information, you may begin with analysis, the second of the ten ERP implementation phases. This will help you determine the business case for ERP implementation, which will outline project goals and how these will be achieved.
This involves conducting interviews, workshops, and surveys with key stakeholders. The team analyzes existing workflows, data structures, and system integrations to determine the optimal ERP configuration. Through this, your business will be able to evaluate the benefits, risks, and costs involved.
Phase 3. Planning
The third of the ten ERP implementation phases requires you to keep a check on the following three domains:
- Resources: You should choose a team that will help you with ERP implementation and further take care of it by ensuring that it is viable for your firm. You can involve a diverse group of people in this part.
- Change management plan: Here you will be laying down a road map to transform your current scheme of management to a better form. You should also include a set of guidelines to follow in the future.
- Budget Forecasting: Keep an eye on how you want to spend your money throughout the implementation so that you do not incur losses in the end.
Phase 4. System Design
In this phase, you should document how the ERP will enable new workflows and processes from the perspective of an end user. Make sure you take feedback from your actual end users to avoid any hiccups in the future due to a mismatch.
The implementation team turns the requirements acquired in the previous phase into a detailed system design during the system design phase. Defining the ERP modules to be installed, designing workflows, developing data models, and establishing interaction points with other systems are all part of this process. The system design phase establishes the groundwork for the ERP solution's actual development and setup.
Phase 5. Development and Configuration
The developers will arrange the chosen ERP software so that it matches your requirements, process flows, and wireframes. This will include a high level of customization to meet the exact requirements of your business. You can also jot down all the knowledge of how you are developing the system.
The implementation team customizes the ERP system according to the established requirements during the development and configuration phase. This includes writing custom code, configuring modules, customizing user roles and permissions, and creating workflows. To minimize customization and future upgrade hassles, establish conformity with industry best practices, and exploit the ERP system's standard features.
Phase 6. Data Migration
Data migration is the act of transferring your present business data to the new system. It is a crucial element of the ERP implementation phases. Your data may include things such as account history and employee or product data among others. You can migrate your data using the given steps:
- Converting and collecting data from previous software: Each system is different from the other and before starting with the data transfer or migration you should collect it. You should try and remove outdated information, which is no longer in use so that the new system utilizes the actual state of your business in the best manner.
- Review and approve: Human beings can make errors and therefore, it becomes essential to confirm that the migrated data is accurate. This is much better than facing serious issues later. You can spend some time in this domain before taking any major steps.
Phase 7. Testing
Testing is another important part of the ERP implementation phases. You can conduct three kinds of tests, depending on what seems better to you.
- Technical Test: In this test, you will be able to ensure that the code provided by the vendor is not faulty. If your code is faulty, your software will fail. You can either make your internal IT department conduct this test or pay a third party to do so.
- Functional Test: In this test, you have to ensure that all promises made by you to yourself are met. You can use the checklist that you created during the planning phase to do so and arrange a point-wise demonstration as well.
- User Acceptance Test: Your project team will conduct this test. You should involve people having in-depth knowledge for this purpose. Confirm auto backups, be prepared for configuration changes and keep buffer time for adjustments.
Phase 8. Training and User Acceptance
In this phase, your employees will get to learn how they can use the new software that you have employed. For this purpose, you should train them well so that they become familiar with the technicalities of the ERP system.
The implementation team provides comprehensive training to end-users, including system navigation, data entry, reporting, and troubleshooting. Training can be conducted through workshops, online tutorials, and documentation. User acceptance is closely monitored, and feedback is collected to address any concerns or areas for improvement.
Phase 9. Deployment
You can carry out the deployment of ERP implementation phases in several ways:
- All at once: You can deploy all the functions and completely transform the working of your company right away.
- Phased: This will be a phased deployment and the system will be broken into smaller modules or units and launched singly.
- Parallel: Here both, the parent system and the ERP system will work simultaneously, till the new software starts working well.
Phase 10. Support & Updates
After the implementation is done, you need to ensure proper maintenance of your system for its best performance. You will also be able to evaluate your success post-implementation through this. Talk to the developer and find out if they provide regular updates and maintenance facilities or not. You must keep investing in this domain for a smooth ERP as well.
ERP Implementation Phases Summary Table
| Phase | Key Tasks | Focus for Success |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Initiation and Discovery | Gather information on current systems and processes, Create a discovery team with key stakeholders | Ensure thorough research and collaboration between departments |
| Phase 2: Requirement Analysis | Conduct interviews, workshops, and surveys, Analyze workflows, data, and system integration | Define clear project goals and evaluate benefits, risks, and costs |
| Phase 3: Planning | Assemble the implementation team, Develop a change management plan, Perform budget forecasting | Align resources, ensure proper change management, and maintain control over budget |
| Phase 4: System Design | Create system design and workflow documentation, Define ERP modules and design workflows | Get end-user feedback to ensure the design meets actual needs |
| Phase 5: Development and Configuration | Customize the ERP system, Configure modules and create workflows, Establish user roles and permissions | Minimize customizations and follow industry best practices |
| Phase 6: Data Migration | Collect and convert data, Clean outdated data, Verify the accuracy of migrated data | Focus on data accuracy and ensure only relevant data is transferred |
| Phase 7: Testing | Conduct technical tests, Perform functional tests, Run user acceptance tests | Ensure system stability, performance, and end-user satisfaction |
| Phase 8: Training and User Acceptance | Train employees on system usage, Monitor user acceptance and gather feedback | Provide comprehensive training and address user concerns |
| Phase 9: Deployment | Deploy ERP system in chosen method: all at once, phased, or parallel | Choose a deployment strategy that fits the business needs and minimizes disruption |
| Phase 10: Support & Updates | Implement ongoing support, Plan for regular updates, Track post-implementation success | Maintain system performance and continue investment in support and updates |
How to Successfully Carry Out ERP Implementation – The Process and Plan
There are 17 major steps for ERP implementation, which you must abide by.
- Define the scope of ERP implementation: Write the objectives of your project, anticipate all risks involved, and assign roles to a team.
- Select an ERP system: There are three kinds of ERP systems: custom-built systems, cloud-based systems, and customized ERP systems.
- Draft a project plan: Be logical with your plan and involve stuff like your goals, planned methods, and end-case studies, among others.
- Time taken for ERP implementation: Be patient, and know that generally, the process of ERP implementation takes around 4 to 8 months.
- Define the steps involved: Understand the goals and needs of your business to define steps in a better manner.
- Create a change management plan: You must begin by planning out the plan of ERP implementation in simple steps and then delegating work based on expertise and not seniority.
- Work on an achievable goal: You need to create a schedule for yourself that is urgent but also achievable. Remember not to make tall claims or goals that cannot be achieved with the given resources.
- Communication: To improve communication, you can start by scheduling an organized meeting with all your IT partners. Another thing that you can do is avoid changes in the team.
- Predict costs and budget: Estimate your expenses and draft a budget. Your actual expenses may exceed the estimates, but you can avoid this by being careful about hidden costs.
- Arrange mid-way approvals: Rather than keeping the entire process to be improved in the end, you should try to approve the actions of your employees frequently.
- Plan testing: You can test the ERP system through three kinds of tests: technical tests, functional tests, and user acceptance tests.
- Data migration: You can ensure smooth data migration through two steps: first, converting and collecting data from previous software; and second, reviewing and obtaining approvals.
- Be prepared for change: You must comprehend that mere paperwork does not change the functioning of your business automatically. So you should indulge the employees in the workings of your new system.
- Training: You may train your employees either on the ground, that is, face-to-face, or through e-learning.
- Plan before going live: You should plan the deployment through hardware synchronization, frequent tests, and data migration confirmations.
- Support & Maintenance: Work with your developer and ensure that they are available round the clock, in case of any need.
- Evaluate success: Ask yourself whether you can achieve your goals through this ERP implementation or not. Find out if there have been any improvements or not.
How Other Leading Brands Achieved ERP Transformation
ERP Implementation is a daunting task for growing organizations that are looking for this transformation. Let us find out how big brands took out their ERP implementation into different phases which were successful.
SAP Implementation at Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola, a renowned beverage company, embarked on an ERP implementation project to streamline its global operations. The phases included project initiation, requirement analysis, system design, development and configuration, testing and quality assurance, training, and user acceptance, data migration, and go-live. Coca-Cola successfully implemented SAP ERP, enabling better inventory management, supply chain visibility, and financial reporting across its global network.
Oracle Implementation at Amazon
Amazon, the world's largest e-commerce company, implemented Oracle ERP as part of its strategy to enhance operational efficiency. The implementation phases involved project initiation, requirement gathering, system design, configuration and customization, testing and quality assurance, training, data migration, and going live. Oracle ERP empowered Amazon with real-time insights, streamlined order management, and improved financial controls.
Microsoft Dynamics Implementation at L'Oréal
L'Oréal, a leading beauty and cosmetics company, underwent an ERP implementation using Microsoft Dynamics. The implementation phases included project initiation, requirement analysis, system design, customization and development, testing, training, data migration, and go-live. Microsoft Dynamics helped L'Oréal optimize its supply chain, streamline product lifecycle management, and improve financial visibility across its global subsidiaries.
SAP S/4HANA Implementation at Adidas
Adidas, a renowned sports apparel manufacturer, implemented SAP S/4HANA ERP to enhance its operational efficiency. The implementation followed phases such as project initiation, requirement gathering, system design, configuration, testing and quality assurance, training, data migration, and go-live. SAP S/4HANA enabled Adidas to streamline its supply chain, improve inventory management, and gain real-time visibility into its sales and financial data.
NetSuite Implementation at Airbnb
Airbnb, a popular online marketplace for vacation rentals, opted for NetSuite ERP implementation to support its growing business operations. The implementation phases encompassed project initiation, requirement analysis, system design, customization, testing and quality assurance, user training, data migration, and go-live. NetSuite helped Airbnb automate its financial processes, improve financial reporting, and streamline vendor management.
Types of an ERP Implementation Plan
There can be any categorization of types of ERP implementation. Considering the current industry standards followed in implementing a cloud-based ERP implementation, there are three kinds. They are Express ERP implementation, Standard ERP implementation, and Advanced ERP implementation.
| Project Type | Express Implementation | Standard Implementation | Advanced Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Approach | Streamlined and accelerated | Comprehensive and customized | Highly tailored and advanced |
| Project Duration | Shorter timeframe | Moderate timeframe | Longer timeframe |
| Customization Level | Minimal customization | Moderate customization | Extensive customization |
| Deployment Speed | Rapid deployment | Controlled rollout | Gradual deployment |
| Business Requirements | Standard processes and requirements | Specific business needs | Complex and unique requirements |
| Data Migration | Basic data migration | Data migration with transformation and mapping | Extensive data migration and integration |
| Testing and Training | Limited testing and training | Comprehensive testing and user training | Rigorous testing and advanced user training |
| Scalability | Limited scalability | Moderate scalability | High scalability and adaptability |
| Maintenance and Support | Standard support and maintenance | Ongoing support and maintenance | Continuous improvement and optimization |
Based on your current business process, requirements, and different disjointed systems and departments, you can choose your implementation process.
Components of ERP Software for Implementation Process
The components of an ERP depend on the needs of the organization but some features are intrinsic to each ERP. Some major components are finance, human resources, logistics and manufacturing, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
- Financial management: Tracks all financial transactions, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, costs, budgets, and forecasts.
- Human resources: Manages all employee-related information, including payroll, benefits, performance reviews, and training.
- Manufacturing and logistics: Manages the production process, from ordering raw materials to shipping finished goods.
- Supply chain management: Manages the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers.
- Customer relationship management: Manages all customer interactions, from sales to service.
- Custom component: A lot of ERP implementation consulting companies, like Captivix, also help in building custom modules for your ERP needs. It can sync with custom mobile apps or web apps for better monitoring and forecasting of business operations.
Make sure that your CIO is well-informed about what modules can be useful, customized, or ignored, based on your business needs.
Tips for Selection and ERP Implementation
Here are some tips to ease the process of selection and ERP implementation:
- Define objectives and set goals for guidance: Begin by understanding your goals and drafting a plan that keeps them all in mind. Resolve political issues within the firm if any, and ensure that change management processes are going well.
- Maintain the processes: You should rethink how your company works and how you can make it more efficient. Take advantage of the data migration and deployment whenever possible.
- Streamline your data: Know what you are migrating and make sure that it is relevant to your business. Do not overhaul unnecessary data and remember to migrate with utmost care.
- Focus on major needs: You should know what your business actually requires as this will help you find an ideal option for yourself. There is no point in investing in something that does not matter at the moment.
- Plan ahead of time: Conduct this part with your vendor by asking them about the future support that they will be providing. Check whether the system will grow with your business and whether it can be customized or not.
- Schedule demos in the beginning: Ask your vendor to give you demos of the system you are choosing, to understand whether it will suit your needs and work to your advantage or not.
- Choose a viable vendor: Be sure of whom you are dealing with. Choose a vendor who has a reputation in the market and industry expertise, to make the ERP implementation smoother.
- Prioritize end-users: While selecting a system, keep the end-users in mind. Check if it will work the best for them or not because the end-users will be handling its activities and deciding how it will work for your business.
- Integration: The ERP should work in consonance with the other apps and software involved in your business to ensure the smoother working of the business.
- Be sure about customizations: Know whether you would like to customize your system or standardize it. To be sure, a lot of companies these days are opting for standardization.
- Low-code works the best: Low-code can help you deploy any improvements quite safely and ensure the efficiency of work. These do not impact the core of the ERP system.
Best Time for ERP Implementation
The best time varies based on factors like the company, industry, and business cycle. Usually, the best time for ERP implementation is during the slower periods of business or the off-season. Another factor to keep in mind before starting the process is the stability of your business.
If you try to implement ERP in the middle of the night, due to some random idea that you got, it will only result in a haphazard for your business. Therefore, analyze the possible chances or rate of success of implementing the software before taking any decision.
How Long Should an ERP Implementation Process Take?
The duration of an ERP implementation process can vary greatly depending on the complexity of your project and the size of your business. For small to medium-sized businesses with straightforward requirements, the process might take between 4 to 8 months. Larger enterprises with complex needs may require 12 to 24 months or even longer.
Never rush the process for the sake of speed, as a thorough and well-executed implementation will yield the best results.
ERP Implementation: Costs Involved
ERP implementation costs can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the scope and complexity of your project. Key cost factors include:
- Software licensing fees: The cost of the ERP software itself.
- Implementation services: Consulting, customization, and configuration services.
- Data migration: The cost of transferring data from legacy systems.
- Training: Employee training programs.
- Hardware: Any necessary infrastructure upgrades.
- Ongoing maintenance: Annual support and maintenance fees.
It's essential to budget carefully and anticipate hidden costs that may arise during the implementation process.
ERP Implementation: Best Practices to Follow
Following best practices can significantly increase your chances of a successful ERP implementation:
- Secure executive sponsorship: Ensure you have strong leadership support throughout the project.
- Involve key stakeholders early: Get buy-in from all departments that will be affected.
- Define clear objectives: Know what you want to achieve before you start.
- Choose the right implementation partner: Select a vendor with experience in your industry.
- Focus on change management: Prepare your organization for the transition.
- Prioritize data quality: Clean and validate your data before migration.
- Test thoroughly: Conduct comprehensive testing at every phase.
- Train extensively: Invest in thorough training for all users.
- Plan for go-live support: Have resources ready to address issues after deployment.
Failure Rate and Major Reasons
ERP implementations have historically had high failure rates, with some studies suggesting that 50-75% of projects fail to meet their objectives. Major reasons for failure include:
- Poor planning: Inadequate project planning and scope definition.
- Lack of executive support: Without leadership backing, projects struggle to succeed.
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist new systems and workflows.
- Insufficient training: Users who don't understand the system won't use it effectively.
- Data quality issues: Poor data migration can cripple a new system.
- Unrealistic expectations: Setting unachievable goals leads to disappointment.
- Choosing the wrong vendor: A poor fit between the ERP and your business needs.
- Underestimating complexity: Failing to account for the full scope of the project.
By understanding these risks and planning accordingly, you can significantly improve your chances of success.
Start Implementing Your ERP Solution with Our Guide Today!
This comprehensive guide has walked you through every aspect of ERP implementation, from the initial phases to best practices and common pitfalls to avoid. With careful planning, the right partner, and a commitment to following proven methodologies, your organization can successfully implement an ERP system that drives efficiency, improves decision-making, and supports your business growth.
Ready to start your ERP journey? Contact our team of experts to learn how we can help you achieve a successful implementation.

Divyank Arya
Content strategist and ERP specialist at Captivix, helping businesses navigate digital transformation with actionable insights and proven methodologies.